l Radiation Protection Measures Implemented by Nuclear Power Plant
Ø Nuclear Safety Surveillance
The objectives of nuclear safety surveillance in nuclear power plant are to:
- verify the implementation of safety regulatory requirements;
- perform surveillance on the correction of non-conforming items;
- justify the qualification of the personnel related to nuclear safety;
- ensure that materials, components, structures, systems, and activities are conforming to nuclear safety requirements; and
- ensure reporting of any defect and abnormal event in time.
In China, the National Nuclear Safety Administration (NNSA) requests that the management of nuclear power plant should eliminate unsafe factors of items and activities in nuclear installation in order to protect the site personnel, the public and the environment from possible adverse effects arising from the nuclear installations. NNSA will take enforcement action and order the nuclear power plant to take safety measures or to stop plant activities where necessary.
Ø Processing of Radioactive Effluents Before Release
All gaseous and liquid effluents from nuclear power plant are processed before being released into the environment. Contaminated gases pass through waste treatment systems involving filters and iodine absorbers and are retained in storage tanks for several weeks to allow radioactivity to decay. Radioactive liquids are filtered and further processed in an ion-exchanger or an evaporator. When the effluents meet statutory requirements, they are diluted with large cooling water flow and discharged into the sea.
Sophisticated radiation monitoring and alarm systems are installed at nuclear power plant to assess and control the radioactivity levels of normal releases.
Ø Monitoring and Control of Radioactivity in the Environment
An important part of the nuclear power station is the monitoring of radioactivity levels in air, dust, sea and fresh water, soil and sediment, land and marine plants, and animals in the vicinity of the power station. During the operation, ambient gamma radiation will be continuously measured at some atmospheric monitoring stations away from the nuclear power plant. Regular and automatic sampling for waterborne radioactivity measurement will take place at a liquid discharge monitoring station in the cooling water discharge channel.

Regular Monitoring of Radioactivityin the vicinity of Nuclear Power Plant
For the nuclear power stations at Daya Bay and Lingao, Guangdong, which are about 50 km from Hong Kong, the power stations have respectively set up three atmospheric monitoring stations and four gamma radiation monitoring stations about 1 km and 5 km away from the power stations.
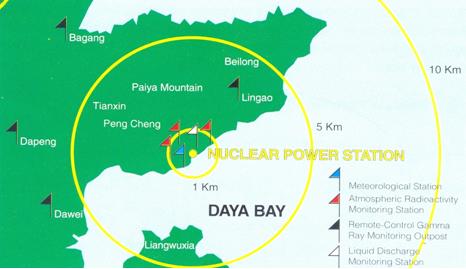
Environmental Monitoring Stations set up by Guangdong Nuclear Power Station
Image Credit : HKNIC